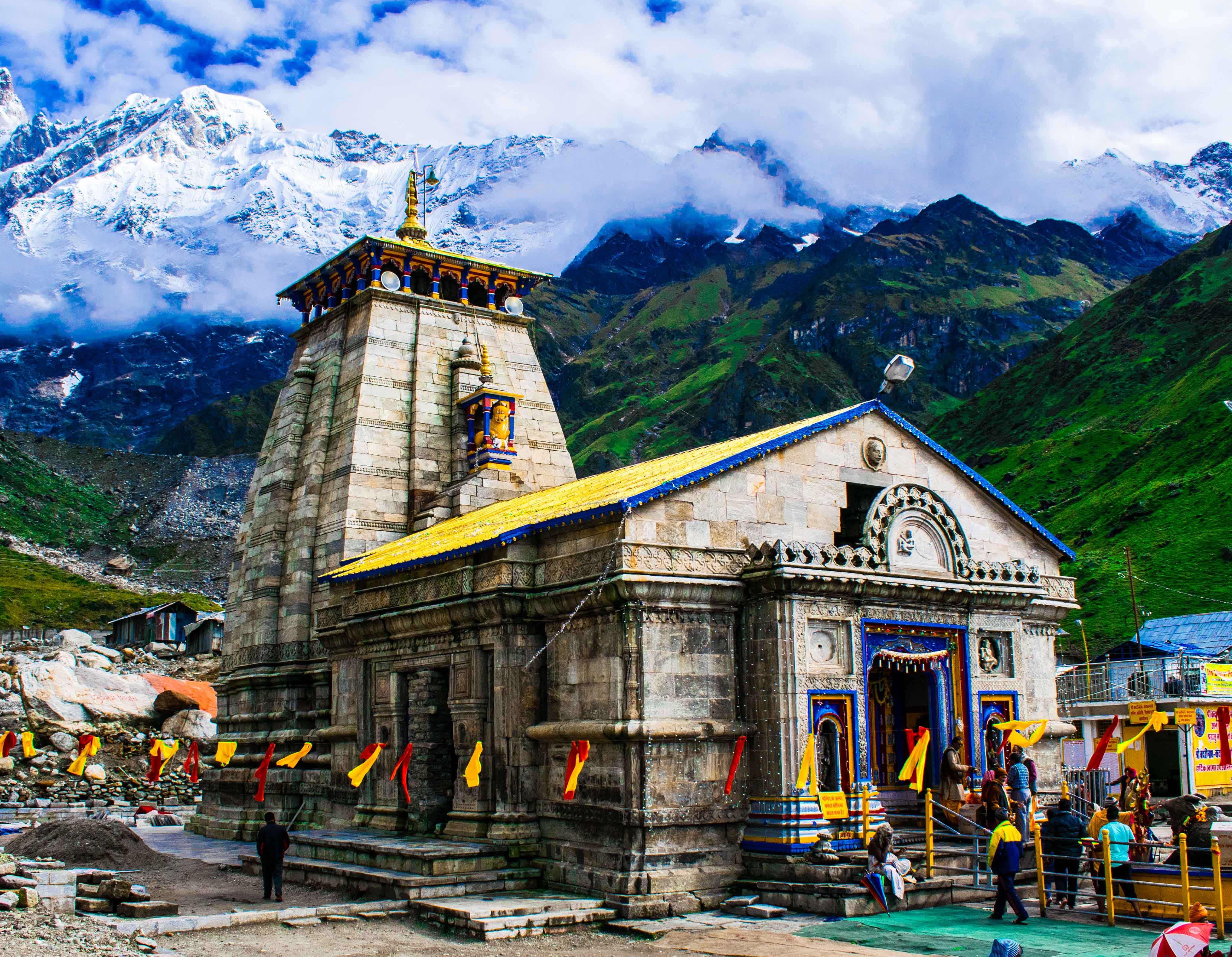
High in the daunting Garhwal Himalayas, at an elevation of about 3,583 meters, sits the ancient Kedarnath Temple, one of the most sacred and revered shrines of Lord Shiva in India. Located in Uttarakhand’s Rudraprayag district, on the banks of the Mandakini River, Kedarnath is esteemed as one of the twelve Jyotirlingas and the highest among them. The temple is also a cornerstone of the Char Dham Yatra, drawing devotees who brave both the natural and spiritual challenges of the Himalayan landscape. Its enigmatic remoteness, mythic past, and profound spiritual significance mark Kedarnath as a destination of transformation, penance, and awe.
The mythic tapestry of Kedarnath is richly woven with legendary episodes that combine cosmic drama and personal redemption. One of the most enduring legends links Kedarnath to the epic Mahabharata. After prevailing over the Kauravas, the Pandava brothers, burdened with the sin of killing their kin, journeyed in search of Lord Shiva to seek absolution. Shiva, unwilling to forgive them easily, disguised himself as a bull, Nandi, and eluded their pursuit, moving through the region now known as Kedar Khand. Bhima, the strongest Pandava, eventually recognized the bull and managed to seize it, but Shiva vanished into the ground, leaving his hump on the surface. This distinctive conical rock became the central lingam of Kedarnath Temple. The tale further describes how other parts of Shiva’s bull form appeared in Tungnath, Rudranath, Madhyamaheshwar, and Kalpeshwar, collectively comprising the Panch Kedar pilgrimage circuit. The episode showcases themes of challenging penance, divine play, and the possibility of redemption.
Another legend highlights the spiritual austerities of the twin sages Nara and Narayana, incarnations of Vishnu, who meditated at Kedarnath for centuries. Their sincere devotion pleased Shiva, who granted them his permanent abode there, affirming the temple’s transformative energy and its power to bestow spiritual merit. The Skanda Purana speaks of Shiva releasing the heavenly water from his matted hair at Kedarnath, further sanctifying the temple as a source of cosmic and earthly purity. Local belief also recalls Shiva himself performing penance at Kedarnath to absolve the sin of Brahma Hatya, the killing of a Brahmin, etching a narrative of redemption and transcendence into the landscape.
Kedarnath Temple endures at the crossroads of myth and history. Although the precise date of Kedarnath’s original construction remains a mystery, legend credits the Pandavas with building the temple after their encounter with Shiva. Historians suggest the present temple may date back over a thousand years, with the earliest reliable records emerging from the 8th century CE.
The 8th-century philosopher and reformer Adi Shankaracharya is believed to have re-established Kedarnath Temple, constructing the structure that stands to this day. His travels, spiritual activism, and temple restoration efforts were pivotal in reviving spiritual traditions across the Himalayas.
Kedarnath has faced the brunt of nature’s wrath, centuries of snow, earthquakes, avalanches, and floods tested its foundation. Remarkably, the temple survived a “mini ice age,” enduring under snow for up to 400 years. Most recently, in 2013, devastating floods nearly destroyed the surrounding town but left the temple largely intact, deepening the sense of divine protection and resilience associated with Kedarnath.
Regional kings, saints, and temple committees have played their parts in preserving Kedarnath through restoration, rebuilding, and ritual continuity. Inscriptions in Pali language and references in ancient texts reveal the temple’s stature as an epicentre of Himalayan worship.
Kedarnath’s architecture is as striking as its setting; solid, austere, and sublimely beautiful against the backdrop of snowy peaks. The temple is built of massive stone slabs, laid over a rectangular elevated platform. Its robust geometry reflects both its spiritual intent and the necessity to withstand severe climate extremes. Locally quarried grey stones handle the weight of snow and ice, lending strength and longevity. The holy garbhagriha, the inner sanctum, is accessed by broad, steep steps. The lingam, worshipped as a conical natural rock formation, lies at the heart of the temple; this form is unique, symbolising Lord Shiva’s hump. The inner sanctum walls are adorned with figures of deities and mythic scenes, connecting architecture to religious storytelling. The temple is fronted by a pillared hall and topped by a modest shikhara or spire, epitomising the Himalayan style found in the region’s sacred architecture, as also seen at Tungnath and Madhyamaheshwar. Despite its antiquity, the temple’s design reflects sophisticated understanding of structural engineering, surviving heavy snow, landslides, and earthquakes, with natural geological features incorporated to maximize stability.
Kedarnath’s spiritual rhythm pivots on daily worship, community celebrations, and seasonal rituals dictated by the Himalayan climate. Priests conduct abhisheka, bathing the lingam with water, milk, honey, and flowers amid Vedic chants. The use of naturally sourced Mandakini water is a distinct ritual feature. Devotees offer bilva leaves, rice, and sweets to the lingam, pray for penance and prosperity, and receive prasad as blessing. Due to its high altitude and heavy snowfall, the temple is open to worshippers only between late April and early November. In winter, the idol is ceremonially moved to Ukhimath, where worship continues.
Mahashivaratri is celebrated with great fervour, attracting thousands who participate in night-long vigils, fasting, and communal prayers. The annual opening and closing days are marked by grand ceremonies, music, and mass pilgrim gatherings. Kedarnath’s role as one of the four pillars of the Himalayan Char Dham Yatra, with Badrinath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri, makes its festival calendar integral to regional spiritual life. Community involvement is deep. Local families, priests, and committees organise rituals, maintain facilities, and celebrate cultural expressions with immense hospitality despite the challenging terrain.
Embarking on a pilgrimage to Kedarnath is considered a rite of passage and personal transformation. The journey typically begins at Gaurikund, accessible by road from Haridwar or Rishikesh. Pilgrims then undertake a 16 km trek amidst breathtaking Himalayan views, dense forests, and roaring rivers. Along the route, dharamshalas, camps, local stalls, and mountain guides support pilgrims. The atmosphere is charged with camaraderie, resilience, and shared devotion. Snow-capped peaks, tumultuous streams, wildflowers, and clear skies contribute to a sense of sublime tranquility. Many recount visions, mystical experiences, and moments of peace upon reaching the temple, its setting amplifies feelings of humility and awe. Stories of miraculous survival, especially after the 2013 flood, healing, and prayer fulfillment permeate local lore, reinforcing Kedarnath’s reputation as a place where the divine intervenes directly in human life.
Kedarnath’s influence is far-reaching, nourishing arts, literature, and regional identity. The temple’s legends echo in Sanskrit poetry, devotional songs, and folk tales throughout Uttarakhand and India. Spiritual narratives related to the Pandavas, the Himalayas, and Shiva are central to the region’s storytelling tradition. Musicians compose bhajans dedicated to Kedarnath, performed during big festivals and pilgrim gatherings. Paintings, sculptures, and photographs capture the majesty of Kedarnath, serving both as souvenirs and as artistic inspiration. The architecture itself, stark against the landscape, becomes a symbol of resilience and transcendence. Kedarnath is a pillar of Uttarakhand’s identity and culture. Its survival during natural disasters is seen as a testament to divine protection, forging strong community pride and spiritual confidence.
Today, Kedarnath is a dynamic intersection of spiritual tradition, environmental stewardship, and contemporary tourism. Overseen by the Shri Kedarnath Temple Committee, operations balance daily rituals, conservation, and pilgrim needs. Digital pilgrim registration, enhanced safety protocols, and infrastructural improvements cater to growing visitor numbers. Post-2013, extensive restoration and disaster management initiatives have stabilised the region and safeguarded the temple, collaborating with local, regional, and national agencies. Visitors include domestic and international devotees, trekkers, and spiritual aspirants. The site’s accessibility and amenities are continuously improved. Pilgrim counts swell each season, especially during festival times, fueling local economies and cultural renewal.
Mahashivaratri and Char Dham Yatra bring national attention, media coverage, and boost to regional tourism. Heritage walks, lectures, and spiritual camps enhance both traditional and modern pilgrimage experience.
The Kedarnath Temple stands at the confluence of myth, history, nature, and spirit, an enduring Jyotirlinga of Lord Shiva in the heart of the Himalayas. Its stories of the Pandavas, sages, and Adi Shankaracharya blend with its Himalayan grandeur to create a space transcending generations and boundaries. Through snow and storm, penance and prayer, Kedarnath continues to offer redemption, solace, and empowerment, illuminating the circuit of Jyotirlinga shrines and deepening India’s spiritual heritage.