Growing up, everyone around me spoke Tamil or a Malayalam-tinged Tamil, and I didn’t think anything was amiss. This was my normal. I did hear a slightly different Tamil in the movies, but I didn’t really think too much about it, assuming it was normal for films to sound that way. However, after I moved to Singapore, I experienced culture shock in terms of the Tamil language spoken. The first one came from S and his family, who spoke Tamil, but it was slightly different from what I spoke and had heard spoken all my life. When I asked them, they said their Tamil is the Tamil of the masses, and when they spoke the Tambram dialect, they were teased and made fun of in school and outside, so over the years, the Tambram community in Singapore slowly stopped speaking that dialect and instead switched to the more locally spoken version.
But I am adamant about preserving my heritage, and so far have refused to succumb to subsuming my dialect into the standard Tamil. I don’t speak a lot of Tamil here in Singapore, but when I do, it’s the Tambram Tamil I spoke while growing up. Even with GG & BB, I always spoke to them in this dialect, but given their mostly English language usage, there’s not much hope that they will continue to speak this dialect, and so, at least in my family, the dialect will end with me.
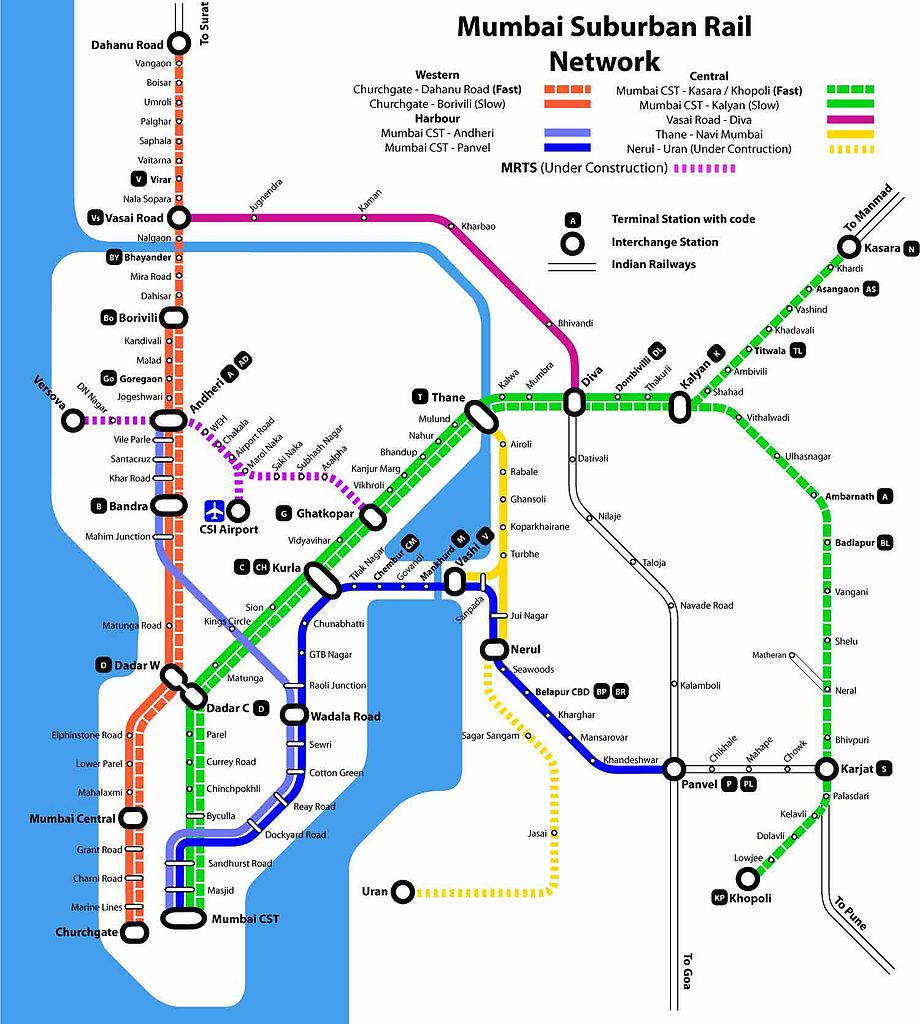
However, the Tamil Brahmins from Tamil Nadu and Kerala who migrated to Mumbai in the 1930s, 1940s, and 1950s have remarkably preserved their Agraharam-style Brahmin Tamil dialects, setting them apart from their counterparts who remained in South India and gradually adapted their speech to local influences. This linguistic retention became a hallmark of communities in areas like Matunga and Chembur, where strong social bonds and cultural traditions reinforced the continuity of dialect and identity across generations.
The migration of Tamil Brahmins to Mumbai was driven by economic opportunities, education, and employment, especially in the early to mid-20th century. Communities from Palakkad in Kerala and Tanjore in Tamil Nadu settled in “urban agraharams” in Mumbai, where they recreated their traditional neighbourhoods with proximity to temples and strong community networks. These settlements fostered a unique microcosm reminiscent of their ancestral villages, creating an environment conducive to linguistic and cultural preservation.
Unlike Brahmins in Tamil Nadu and Kerala, who gradually incorporated elements of regional dialects and accents due to increased interaction with other linguistic communities, those settled in Mumbai retained the Brahmin Tamil dialect, often marked by Sanskritised vocabulary, specific pronunciation patterns, and unique idiomatic expressions. This form of speech, sometimes referred to as “Brāhmik” or “Agraharam Tamil,” remained virtually unchanged for decades because within these tight-knit Mumbai communities, Tamil was spoken largely among themselves, with limited outside influence.
Agraharam Tamil, as spoken by Mumbai’s Tamil Brahmin community, is distinguished by specific lexical, phonetic, and grammatical features that have remained remarkably consistent over decades. Vocabulary features include the extensive use of Sanskrit loanwords or Sanskritised Tamil vocabulary, even for everyday terms (e.g., “upahara” instead of “tiffin” or “snack”); a preference for traditional Brahmin Tamil words such as “aathu” (home) instead of the more common “veetu”; and words and phrases for family, kinship, and rituals that retain old usage (e.g., “aaththu manushaa” for family members).
Pronunciation and phonetic features include the retention of retroflex and “zh” sounds, as in “Tamizh”; here, the older pronunciation is kept alive. Pronunciation is stricter with consonant stress and word-final vowels that are preserved, sometimes more closely adhering to Sanskrit or North Indian phonology (e.g., “Bhāratham” rather than “Bāratham”). The word-final “u” pronounced as a full back vowel in specific contexts.
Grammatical distinctions include specific verb conjugations unique to Brahmin Tamil, such as “varela?” (Are you coming?) versus “vareengla?” in non-Brahmin Tamil. The imperatives use “vaango” (please come) instead of “vaanga”, while the third person plural is often merged with feminine forms, maintaining certain archaic grammatical constructions.
Idiomatic and register features include the frequent use of polite, honorific forms and respectful address stemming from Agraharam culture (words like “mama” and “mami” used for elders or equals), and idioms, greetings, and proverbs rooted in traditional religious or familial contexts.
Social features of the Agraharam Tamil include the use of the dialect within the community for cultural, religious, and domestic discourse, but a code-switch to standard Tamil, English, or Hindi in broader Mumbai society. These features set Mumbai’s Agraharam Tamil apart from both non-Brahmin Tamil and the evolving Tamil of South India, preserving an older, Sanskritised, culturally distinctive dialect in a modern urban setting.
Matunga, Chembur, and similar neighborhoods facilitated daily use of Tamil in religious, social, and family settings. Social gatherings, festivals, and temple activities provided communal reinforcement, allowing younger generations to hear and use the traditional dialect frequently. The cultural insularity of these groups, everyone known as “mama” (uncle) or “mami” (aunt), further insulated their speech patterns from citywide influences, slowing language attrition compared to other urban South Indian populations.
First-generation migrants spoke fluent Palakkad or Tanjore Tamil and often Malayalam, while their children balanced multilingualism, learning Hindi, Marathi, and English for school and work but still using traditional Brahmin Tamil at home. Over time, the third generation adopted more of Mumbai’s urban culture, leading to some language shift, but remnants of the original dialect persist in family conversations, proverbs, and religious contexts.
Brahmins remaining in Tamil Nadu and Kerala were more exposed to local non-Brahmin speech and urban Tamil developments. Political changes and cultural movements led to linguistic adaptation, and many Brahmin families shifted towards regionally dominant accents. In contrast, Mumbai’s Tamil Brahmins maintained a diaspora-style “mini Madras,” echoing older, more formal acculturations of Tamil.
Brahmin Tamil is generally characterised by an elevated use of Sanskrit borrowings, a conservatism in pronunciation and grammar, distinct idiomatic expressions, greetings, and terms, and the retention of certain words, sentences, and intonations associated with temple rituals or traditional family interactions.
These urban agraharams not only preserved language but also traditional food, dress (such as “pavadai” for girls), festivals, and rituals, further reinforcing linguistic distinctiveness. The synergy between physical environment (temple proximity, cohesive housing) and social activities ensured that dialect and culture remained intertwined and resistant to outside change for many decades.
The enduring legacy of the Agraharam-style Tamil dialect among Mumbai’s Tamil Brahmins is a testament to the resilience of cultural identity in the face of migration and urbanization. These communities have preserved not just a way of speaking, but a way of being, deeply rooted in tradition, even as they embraced the cosmopolitan vibrancy of Mumbai.